Assaying and hallmarking of gold is a process of determining the Purity of gold and certifying its quality.
 Assaying is the process of determining the purity of gold by measuring the weight of the metal in a
sample and comparing it to the weight of other metals that may be present. This is typically done
through a process called fire assay, which involves heating a sample of the gold with a flux, which
helps to separate the gold from any other metals that may be present. The resulting sample is then
weighed and analysed to determine the purity of the gold.
Assaying is the process of determining the purity of gold by measuring the weight of the metal in a
sample and comparing it to the weight of other metals that may be present. This is typically done
through a process called fire assay, which involves heating a sample of the gold with a flux, which
helps to separate the gold from any other metals that may be present. The resulting sample is then
weighed and analysed to determine the purity of the gold.
 Hallmarking is the process of certifying the purity of gold through the use of a hallmark, which is a
symbol or mark stamped onto the gold. The hallmark is typically stamped by a government-
approved agency, such as the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), and it serves as an assurance of the
purity and quality of the gold. The Hallmarking system ensures that the gold jewellery that is sold by
weight is of the purity that is claimed by the manufacturer.
Hallmarking is the process of certifying the purity of gold through the use of a hallmark, which is a
symbol or mark stamped onto the gold. The hallmark is typically stamped by a government-
approved agency, such as the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), and it serves as an assurance of the
purity and quality of the gold. The Hallmarking system ensures that the gold jewellery that is sold by
weight is of the purity that is claimed by the manufacturer.
 In India, the BIS is responsible for setting standards for gold and other precious metals, and for
certifying the quality of gold through its hallmarking program. The hallmarking of gold jewellery is
mandatory in India. The hallmarking of gold in India is done under the BIS Act, and the hallmarking of
gold jewellery is done at the Hallmarking Centres or at the BIS-approved Assaying and Hallmarking
Centres.
In India, the BIS is responsible for setting standards for gold and other precious metals, and for
certifying the quality of gold through its hallmarking program. The hallmarking of gold jewellery is
mandatory in India. The hallmarking of gold in India is done under the BIS Act, and the hallmarking of
gold jewellery is done at the Hallmarking Centres or at the BIS-approved Assaying and Hallmarking
Centres.
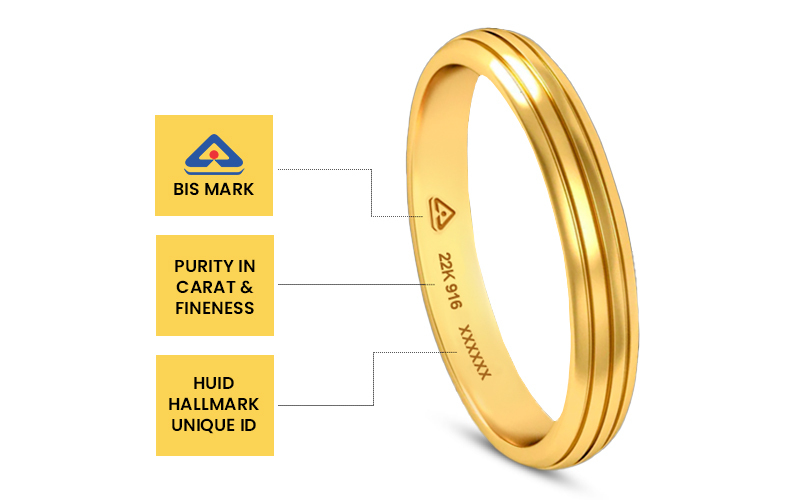
The hallmarking of gold includes the following marks:
- 1. BIS mark
- 2. Purity in Karat
- 3. Assaying and Hallmarking Centre's Mark
- 4. Year of Marking
It is important to note that hallmarking of gold is not only important for consumers to ensure they are getting what they are paying for, but also for manufacturers and sellers to protect themselves against any fraud or false claims about the purity of their gold. Regenerate response
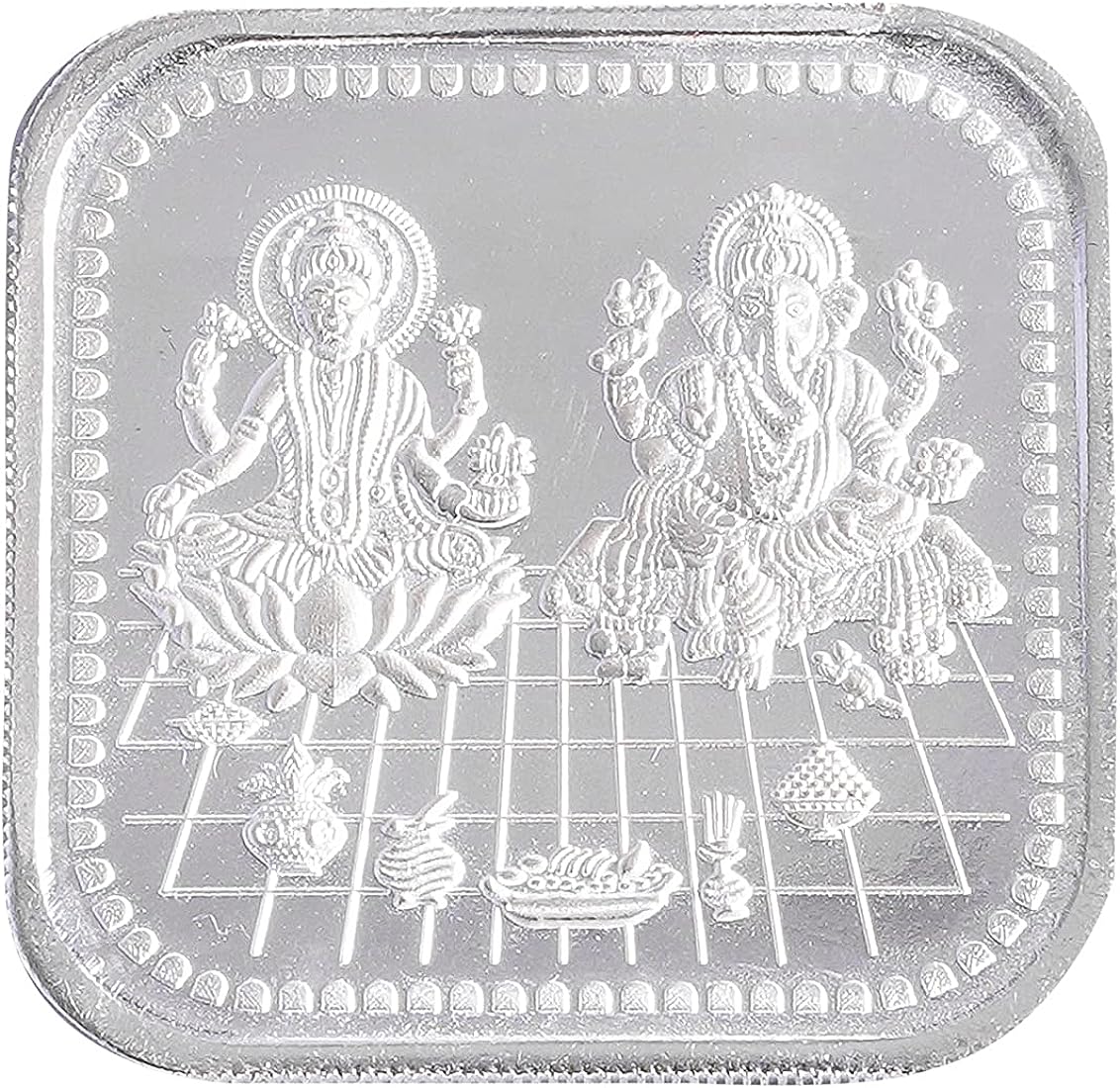
Silver hallmarking is a process of certifying the purity of silver and ensuring that it meets certain standards of quality. The process is similar to gold hallmarking, in that it involves determining the purity of the silver and stamping a symbol or mark on the metal to indicate its quality.
In India, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is responsible for setting standards for silver and other precious metals, and for certifying the quality of silver through its hallmarking program. The hallmarking of silver jewellery is mandatory in India. The hallmarking of silver jewellery is done at the
Hallmarking Centres or at the BIS-approved Assaying and Hallmarking Centres. The hallmarking of silver includes the following marks:
- 1. BIS mark
- 2. Purity in fineness
- 3. Assaying and Hallmarking Centre's Mark
- 4. Year of Marking
The fineness of silver is measured in terms of parts per thousand. For example, silver that is 995 parts per thousand is considered to be 99.5% pure. The standard for silver in India is 925 for Sterling Silver which is 92.5% pure silver and the rest is alloy.
As with gold, hallmarking of silver is important for both consumers and manufacturers/sellers. It helps ensure that consumers are getting the quality of silver they are paying for, and it also protects manufacturers and sellers from any fraud or false claims about the purity of their silver.
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is the national standards organization of India and is responsible for setting standards for gold and other precious metals. The BIS has established standards for gold under the Hallmarking of Gold Jewellery and Gold Articles Regulations, 2000, and the Hallmarking of Gold Jewellery and Gold Articles (Amendment) Regulations, 2021.
The BIS standard for gold is based on the karat system, which is used to express the fineness or purity of gold in parts per 24. For example, 24-karat gold is pure gold with no other metals mixed in, while 18-karat gold is 18 parts gold and 6 parts other metal (such as copper or silver).
The BIS standard for gold includes the following karat values:
- 916 (22K)
- 750 (18K)
- 585 (14K)
- 375 (9K)
The BIS standard for gold also includes a range of other specifications, such as the size and shape of the hallmarking stamp, the location of the stamp on the gold item, and the information that must be included on the hallmarking certificate.
It is important to note that, in order for a gold item to be legally sold in India, it must be hallmarked by the BIS or one of its approved hallmarking centres and must conform to the BIS standard for gold. This is to ensure that consumers receive the quality of gold they are paying for and it also protects manufacturers and sellers from any fraud or false claims about the purity of their gold.
The Indian Standard referred for Gold is IS 1417:2018 (Hallmarking of Gold Jewellery and Gold Articles) which was established by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). This standard is based on the karat system, which is used to express the fineness or purity of gold in parts per 24. IS 1417:2018 covers the hallmarking of gold jewellery and gold articles including the requirements for hallmarking, purity, fineness, Hallmarking Centre, hallmarking stamp, hallmarking certificate and other related information.
The standard defines the following karat values:
- 916 (22K)
- 750 (18K)
- 585 (14K)
- 375 (9K)
This standard is mandatory for gold jewellery sold in India, to ensure that consumers receive the quality of gold they are paying for and it also protects manufacturers and sellers from any fraud or false claims about the purity of their gold.
The IS 1417:2018 standard is reviewed and updated periodically by BIS to ensure that it reflects the current industry practices and technologies.
Testing
Read More
Inspection
Read More
Certification
Read MoreTesting Services
- Drugs & Pharmaceutical Testing
- Cosmetics & Essential Oils Testing
- Medical Devices Testing
- Ayush - Ayurvedic Drug Testing
- Food Products Testing
- Agri Commodities Testing
- Fertilizers and Soil Testing
- Animal Food & Feed Testing
- Water - Drinking Water & Effluent Water Testing
- Industrial Oils and Lubricants & Petroleum Products Testing
- Coal & Coke and Solid Fuels Testing
- Ores & Minerals Testing
- Metals & Alloys Testing
- Plastics, Polymer, Rubber & Rubber Products Testing
- Resins & Adhesives Testing
- Paints, Varnish, Pigments & Surface Coating Testing
- Glass & Ink, Paper & Pulp Testing
- Industrial & Fine Chemicals Testing
- Dyes, Acids and Solvents Testing
- Soaps, Detergents & Toiletries Testing
- Packaging & Packaging Products Testing
- Gold & Silver Assaying & Hallmarking
- Cement, Concrete & Building Materials Testing
- Pollution and Environmental Studies
- Microbiological Assays. Etc.,









