Packaging and packaging products testing
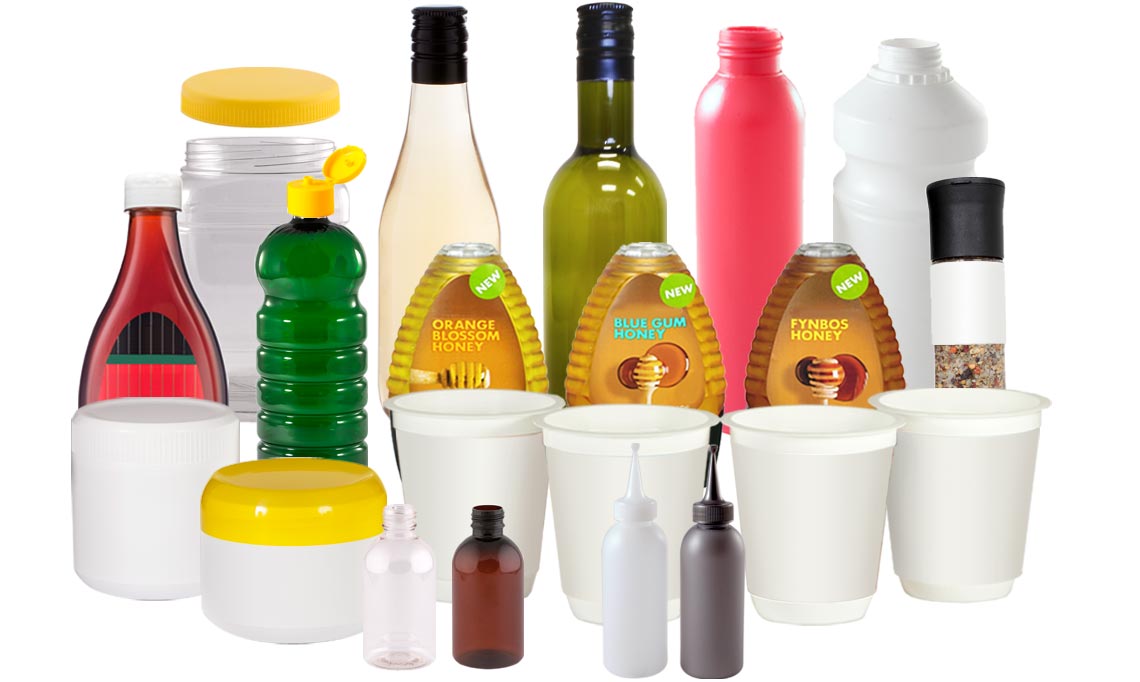 Packaging and packaging products testing is a crucial aspect of ensuring the safety, quality, and integrity of various types of packaging materials and containers. Testing helps manufacturers, retailers, and regulatory bodies verify that packaging meets specific requirements and standards, ensuring that the packaged products are protected during storage, transportation, and use. Here are some common types of testing conducted for packaging and packaging products:
Packaging and packaging products testing is a crucial aspect of ensuring the safety, quality, and integrity of various types of packaging materials and containers. Testing helps manufacturers, retailers, and regulatory bodies verify that packaging meets specific requirements and standards, ensuring that the packaged products are protected during storage, transportation, and use. Here are some common types of testing conducted for packaging and packaging products:
- Physical Testing: This involves assessing the physical properties of packaging materials such as strength, durability, and impact resistance. Common tests include compression testing, burst testing, drop testing, vibration testing, and shock testing.
- Material Testing: This focuses on evaluating the properties and characteristics of packaging materials themselves. It includes tests like tensile strength, elongation, tear resistance, puncture resistance, moisture barrier properties, oxygen and gas permeability, and light transmission.
- Dimensional Measurements: This verifies the dimensions and tolerances of packaging products to ensure they meet the required specifications. It includes measurements such as length, width, height, thickness, and weight.
- Chemical Testing: This examines the chemical composition of packaging materials to identify any harmful substances or contaminants that could migrate into the packaged product. Tests may include extractable and leachable analysis, heavy metals testing, and testing for specific chemicals or additives.
- Print and Label Testing: This evaluates the quality and legibility of printed information on packaging, including barcodes, labels, and product markings. It ensures that the printing is clear, durable, and meets regulatory requirements.
- Environmental Testing: This assesses the packaging's performance under different environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to light. It helps determine the packaging's ability to withstand varied storage and transportation conditions.
- Child-Resistance Testing: This testing focuses on packaging designs intended to prevent accidental access by children to potentially harmful products. It ensures that packaging complies with safety regulations, such as child-resistant closures for pharmaceuticals or household chemicals.
- Shelf-Life Testing: This evaluates the packaging's ability to protect the product over its intended shelf life. It includes tests for barrier properties, light sensitivity, moisture resistance, and stability under different storage conditions.
PACKAGE TESTING AND QUALITH EVALUATION:
Types of Packages used: Shipper Packs ( Corrugated Boxes) Mono Cartons , Bottles ( Glass/Plastic) Blister & Strip , Collapsible Tubes. Etc.
Materials used in Packaging: Paper, Board, Plastic, Glass & Metals etc.
Testing & Evaluation of Plastic Flexible Materials: Thickness, Tensile Strength & Elongation, Peel/Stripping Strength, Heat Seal Strength, Dart Impact Test, Gloss ( 20, 60 & 85 Deg) & Haze, WVTR & OTR, Co-Efficient of Friction ( Static & Dynamic) , Migration Test and Specific Polymeric Materials for Safe Use in contact with Food Stuffs/ Pharmaceuticals, RoHS,
QUALITY EVALUATION OF PLASTICS RAW MATERIALS: Identification ( FT-IR) , Density, Melt Flow Index ( MFI) , Melting and Glass Transition Temperature DSC
Quality Evaluation of Paper & Paper Board:
CHEMICAL : Grammage, Cobb Test, Moisture Content, Ash Content, pH, Chloride Content, Sulphate Content,
OPTICAL : Gloss, Brightness, Opacity,
MECHANICAL : Thickness/Caliper , Bursting Strength, Tensile and Tear Strength, Folding Endurance , Smoothness & Porosity, Scuff Proofness, Surface Strength etc.,
Quality Evaluation of Plastics & Rigid Containers:
Leakage Test- Closure leakage Test, Vibration Leakage Test, Air Pressure Leakage Test, Vacuum Leakage Test, Hydrostatic Pressure Test, Test for Compatibility, Torque Test,
Quality Evaluation of Glass containers:
Annealing Test, Thermal Shock, Pressure Test, Impact Test, Density Test, Capacity, Dimensions, Brimful Capacity, Verticality of Bottle.
Quality Evaluation of Metal:
Mass of Tin & Lacquer Coating, Lacquer Curing Test, Lacquer Continuity, Thickness ( Total, Tin & Lacquer)
Quality Evaluation of Transport Worthiness of Filled packages:
Road, Rail, Sea, Air, Inland Water ways. As per Standard IS 7028 ( Part -2)- Vibration Test, Rolling Test, Inclined Impact Test, Drop Test,
All the above test as per Indian and International Standards such as IS, ASTM,ISTA TAPPA etc.
 These are just a few examples of the testing performed on packaging and packaging products. The specific tests required will depend on the nature of the product, industry standards, and regulatory requirements governing the intended use of the packaging. Testing laboratories specializing in packaging and materials science can provide more detailed information and guidance based on specific needs.
These are just a few examples of the testing performed on packaging and packaging products. The specific tests required will depend on the nature of the product, industry standards, and regulatory requirements governing the intended use of the packaging. Testing laboratories specializing in packaging and materials science can provide more detailed information and guidance based on specific needs.
- Color and Appearance Testing: Paints are tested for color accuracy, consistency, and appearance. This may involve visual assessment, color matching using spectrophotometry or colorimetry, and evaluation of gloss or sheen levels.
- Adhesion Testing: Adhesion testing determines the bond strength between the paint and the substrate. Techniques such as cross-cut or pull-off tests are used to assess the coating's ability to adhere to the surface.
- Film Thickness Measurement: The thickness of the paint film is measured to ensure it meets the required specifications. Dry film thickness gauges or micrometers are commonly used for this purpose.
- Drying Time and Curing Evaluation: Paints are tested to determine their drying time and curing characteristics. This involves assessing the time required for the paint to dry to touch, achieve full cure, or become resistant to solvents.
- Abrasion Resistance Testing: Abrasion resistance testing evaluates the ability of the paint to withstand wear and abrasion. Methods like Taber abrasion testing or falling sand tests are used to measure the paint's resistance to abrasion.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Paints may undergo chemical resistance testing to assess their resistance to various chemicals, solvents, or cleaning agents. Exposure tests or immersion tests in specific chemicals can evaluate the paint's resistance.
- Weathering and UV Resistance Testing: Outdoor paints need to withstand weathering and UV exposure. Accelerated weathering tests, such as UV exposure, humidity cycling, or salt spray testing, are performed to evaluate the paint's durability and resistance to environmental factors.
- Scrub Resistance Testing: Scrub resistance testing assesses the ability of the paint to withstand scrubbing or cleaning without deteriorating. This is done using scrub resistance machines or manual scrub tests.
- Water Vapor Permeability Testing: Water vapor permeability testing helps determine the paint's ability to allow moisture to pass through. Techniques like the cup method or gravimetric method assess the paint's permeability to water vapor.
- Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Testing: VOC testing measures the amount of volatile organic compounds emitted from the paint. This testing ensures compliance with environmental regulations and health standards.
- Quality Control and Compliance: Paint testing often involves following specific industry standards, such as those set by ASTM International or ISO. Compliance with these standards ensures consistent quality, performance, and adherence to regulations.
The specific tests and protocols may vary depending on the type of paint, its intended use, and the applicable regulations or standards. Manufacturers or industry organizations provide guidelines for testing procedures and acceptance criteria.

Testing
Read More
Inspection
Read More
Certification
Read MoreTesting Services
- Drugs & Pharmaceutical Testing
- Cosmetics & Essential Oils Testing
- Medical Devices Testing
- Ayush - Ayurvedic Drug Testing
- Food Products Testing
- Agri Commodities Testing
- Fertilizers and Soil Testing
- Animal Food & Feed Testing
- Water - Drinking Water & Effluent Water Testing
- Industrial Oils and Lubricants & Petroleum Products Testing
- Coal & Coke and Solid Fuels Testing
- Ores & Minerals Testing
- Metals & Alloys Testing
- Plastics, Polymer, Rubber & Rubber Products Testing
- Resins & Adhesives Testing
- Paints, Varnish, Pigments & Surface Coating Testing
- Glass & Ink, Paper & Pulp Testing
- Industrial & Fine Chemicals Testing
- Dyes, Acids and Solvents Testing
- Soaps, Detergents & Toiletries Testing
- Packaging & Packaging Products Testing
- Gold & Silver Assaying & Hallmarking
- Cement, Concrete & Building Materials Testing
- Pollution and Environmental Studies
- Microbiological Assays. Etc.,









